What is Non Destructive Testing
- Apr 30, 2016
- 4 min read
Non destructive testing (NDT), Non Destructive Evaluation (NDE)
encompass a testing process whereby various materials, components or assemblies are tested for discontinuities, or differences in characteristics without destroying the serviceability (useability) of the part or process. In other words, when the testing company is done with their testing, the part
or component is not damaged and can still be used. Some common uses of NDT are for manufacturers to test weldings or for cracks in metal or thickness and consistency in metal manufacturing. The automobile industry uses non destructive testing to test tolerances in ball bearings, crank shafts and other components under stress. The medical industry has probably seen the most advancement through the use of this technology. Innovations in the field of nondestructive testing have had a profound impact on medical imaging, Just think of the x-ray and MRI including echocardiography, medical ultrasonography, and digital radiography.
According to Wikipedia, the most common Nondestructive testing (NDT) methods include "ultrasonic, magnetic-particle, liquid penetrant, radiographic, remote visual inspection (RVI), eddy-current testing, and low coherence interferometry. NDT is commonly used in forensic engineering, mechanical engineering, petroleum engineering, electrical engineering, civil engineering, systems engineering, aeronautical engineering, medicine, and art. In the world of infrastructure testing nondestructive testing is in fact the deployment of todays technology to examine todays infrastructure.
For our purposes we are going to focus on the non destructive testing as applies to todays infrastructure. These infrastructure include the concrete and steel structures that make the modern world work. Highways, Roadways, Tunnels, High Mast Light Poles, Bridges, Dams, Buildings, Parking Garages and more.

The nondestructive testing or evaluation of worldwide infrastructure is in fact just the re deployment of today technologies to test these infrastructures utilizing methods that lean toward or are completely both non invasive and as non subjective as the current technology allows. The roadways that transport you to work, the bridges that help send you over waterways, the tunnels, highway systems and ports that bring us our food, clothing and luxury items.
Todays infrastructure is ageing. In the US alone there are over 60,000 bridges that are currently failing. Read more here. The life of these structures, the money and resources that are put into design and construction can easily be minimized if non destructive testing methods are adopted early on. As technology continues to improve, the easier it becomes to detect problems early on and make smaller repairs that can extend the life of these assets, save millions of dollars for federal and state governments, protect the lives of our citizens and keep economies moving.
Testing of most concrete and steel structures are still conducted subjectively. Meaning a person will go to the bridge and visually look at those post tension cables that are holding up the bridge that you are driving across and make notes if there are any problem areas. Engineers then come and bore holes into those problem areas to see what the issues are. Once you bore into a structure you most certainly weaken that structure further. You also allow air and moisture into the concrete or post tension cable which will further deteriorate those structures over time. If you send 10 inspectors to do a subjective test, you will most likely get ten different results.
How does that work for a concrete structure? Does it even make sense today that we wait until we see a crack in the concrete to know that there is an issue. Why aren't we peering into the concrete or at the very least utilizing todays technology to better assess cracks in order to make repairs earlier. Monitoring crack progression over time is one way that bridge cracks can be monitored today to determine where problem areas are beginning to appear.
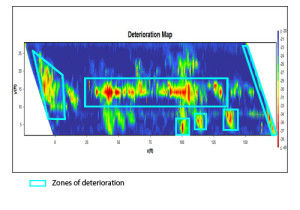
NDT can be utilized to determine delamination and look for defects in concrete. With electromagnetic waves a company like IPC re-configured the interpretation software to be able to investigate the structural composition of concrete elements. This includes that reinforcement of construction elements, bridges, dams, the ability to view connectors and anchors, look for localisation of damaged areas for moisture,cracks, faults and delamination. Their proprietary reports offer the asset managers a detailed inside look at the structure being assessed without further damaging the structure. This is non subjective or actual proof of what is wrong and where the issues exist that have to be repaired.
IPC Infrastructure Preservation Corporation leads the way in adopting existing technology and engineering and patenting new technology and processes specifically designed to better utilize non-destructive testing methods for todays infrastructures.
Some of these patented devices can peer through steel and concrete to determine flaws in the post tension cables that hold up our bridges and roadways, assess weight loads on our bridges and highways and test for concrete cracks and monitor their progression over time.

IPC's equipment and experience can help determine problem areas and even forecast further deterioration, delamination and the life expectancy of certain vital structures.
By employing NDT methods diligently economies will thrive, cost to human life will be minimized and budgets can be utilized in other needed areas like education and schools. For more information contact info@infrastructurepc.com




































Comments