What is Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR)
- Doug Thaler

- Apr 24, 2016
- 3 min read
Ground penetrating radar (GPR) is a non-destructive geophysical

method that produces a continuous cross-sectional profile or record of subsurface features, without drilling, probing, or digging. The GPR cross-section shows the ground surface at the top of the profile, and the reflections of subsurface geologic units and objects to a certain depth at the bottom. Ground penetrating radar (GPR) profiles are used for evaluating the location and depth of subsurface items specifically in the utility and construction industries to plan for building, locate utilities and to investigate the presence and continuity of natural subsurface conditions and features.

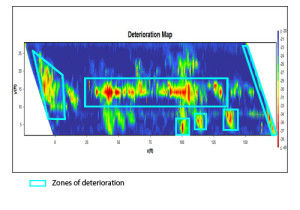
IPC, Infrastructure Preservation Company reconfigured a standard ground penetrating radar unit modified the software to look for deterioration and defects in road surfaces, highways and bridge decks. The precision tuning allows IPC to determine voids and locate delamination and de-bonding of concrete that can lead to rapid deterioration of highways and bridges.
IPC's inspection methods locate problem areas that need to be attended to by the asset manager. Our proprietary inspection reports help the engineering firm pinpoint the areas of concern and prove the urgency of a required repair to the Department of Transportation or the asset owner
IPC's (Infrastructure Preservation Corporation) GPR process can quickly create a more efficient type of data collection in addition to the reduction of disruption drives significant benefits, both in the form of reduced inspection costs as well as the increased precision in locating areas of concern, helping to determine load rates, deterioration, delamination, etc..
One alternative to IPC's method and one that improves precision would be to employ a jackhammer, or in the case of bridge decks using traditional chain dragging - these techniques cannot exactly be called "non-destructive". and in fact add to the deterioration of the structure being tested.
A Brief Overview of how GPR Works
Ground penetrating radar (GPR) is a non-destructive geophysical testing method that produces a continuous cross-sectional profile or record of subsurface features using radar and without digging, probing, or drilling (destructive testing methods). The GPR cross-section shows the ground surface at the top of the profile, and the reflections of subsurface geologic units and objects going to a certain depth at the bottom of the image.
Ground penetrating radar sends a radar pulse into the ground. A part of the penetrating wave is reflected by interference or objects with a variety of dielectric properties different from that of those surrounding it. These reflections are converted into electrical signals. The recorded reflections can be analysed in terms of shape, travel time and signal amplitude to provide information about the size, depth and properties in relation to the material object. With IPC interpretation software, this enables a good identification of reinforcing bars (rebar), thickness of slab, asphalt-concrete overlay, prestressing cables, cable ducts, zones of varying moisture content and thickness of slabs, different concrete, plastic spacers and a very good assessment of large voids and delamination in concrete.

To simplify, Ground Penetrating Radar is a type of non destructive testing that sends a tiny pulse of energy into a material and recording the time and strength that is required for the return of that reflected signal. A scan or a series of pulses over a single area will produce a reflection of the dielectric properties from the material it leaves. In other words it will produce a different signal from wet sand that has a dielectric of 30 to limestone that has a dielectric of 7. The software interprets the signal creating a type of underground mapping that through IPC's software can show problem areas that need immediate attention as well as help assess deterioration over time.
Ground penetrating radar (GPR) profiles are used for evaluating the location and depth of buried objects, frequently used to locate underground utilities and to investigate the presence and continuity of natural subsurface conditions and features.
In many countries around the world NDT is required by law prior to coring and cutting in concrete as well as for Quality Control of new structures. The detailed real-time data and the high display resolution allow the development of accurate structural profiles capable of supporting critical technical decisions directly in the field.
IPC by reconfiguring the GPR's software can provide detailed assessment reports that show early stage deterioration and delamination. For more information go to http://www.infrastructurepc.com or email info@infrastructurepc.com.






































































Comments